-
News & Trends -
Sales -
Marketing Related Topics -
B2B Software Guides Related Topics -
Free Tools & Resources -
- About Us About Us


Product positioning is a marketing and development strategy that entire companies use to control how their solution is perceived by their target market using a key differentiator. Ultimately, it’s presenting, and proving, how your solution solves a problem better than its competition. Successful positioning requires a mix of influence from marketing and sales teams working together to ensure their brand message is cohesive with their customer experience.
Businesses deploy product positioning strategies by creating a brand identity that distinguishes their solution from its competitors. There are two methodologies at the core of product positioning: relative and absolute. Relative positioning describes how your solution does something better than its competitors, whereas absolute positioning specifies how your solution does something that its competitors can’t.
All product positioning strategies use either relative or absolute positioning when presenting the unique selling proposition (USP), or key differentiator, of their solution to their target market. The most common strategies are based in pricing, characteristic, quality, or convenience product positioning. You’ll use this to influence how you’ll carry out your own product positioning in your marketing and lead nurturing techniques.
Once you have a product positioning procedure in place with your brand, your customers should have a consistent experience when dealing with your solution from beginning to end. This will directly impact the success your brand sees by increasing product awareness, revenue, and overall customer satisfaction.
Along with all the reasons product positioning is beneficial to your brand, there’s more information to consider before diving into creating your own product positioning. This consists of insight into the most common positioning strategies, and expert tips in how to build your own.
It’s important to enforce product positioning into your brand because it helps shape your entire company’s approach to how you market and sell your solution. Giving useful insight into your buyers, direction for marketing and selling methods, and an increase in customer satisfaction, retention, and revenue are just a few benefits you can see from implementing a product positioning policy.
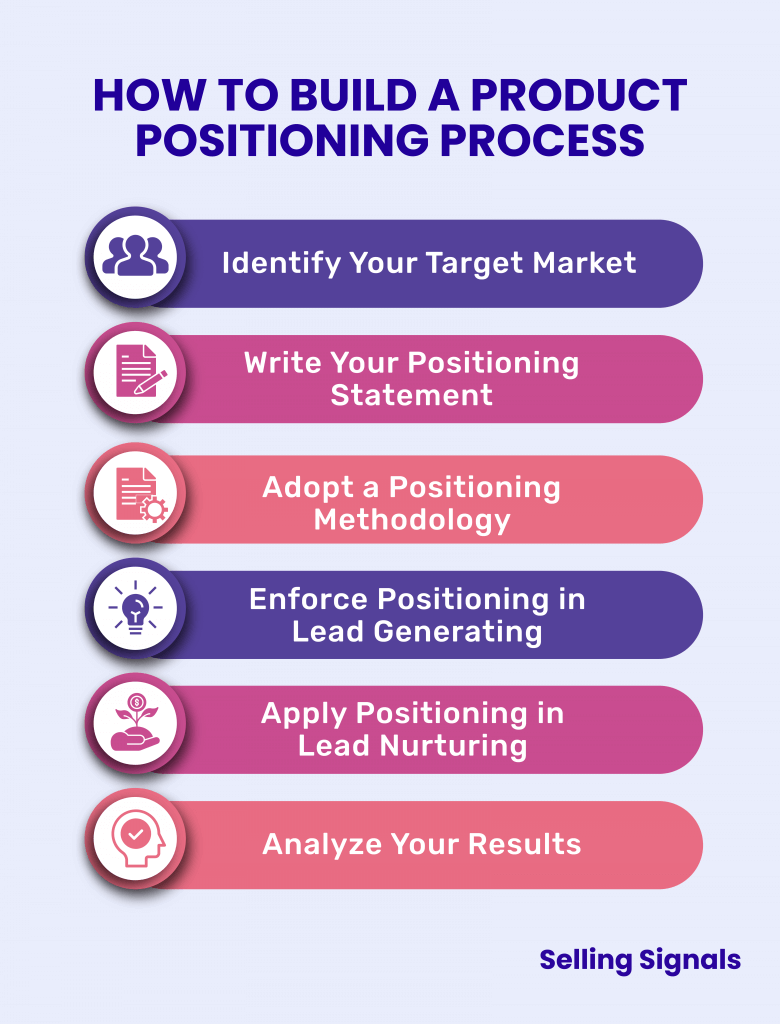
To begin implementing product positioning into your brand, you first need to understand your target audience inside and out. Start by building a customer profile with data-backed insight into their demographics, technographics, and overall approach to buying solutions like yours. Having this insight into how your target market operates ensures you’re building your brand identity on a strong foundation.
With a product positioning game plan in place, marketing and sales teams are given a clear outline as to what problem their customers have and how their product solves it. Using a positioning statement, salespeople know what makes their product stand out, and can use that information when nurturing leads and closing deals. Entire marketing campaigns and selling strategies can be formed from effective positioning.
With the help of strong product positioning, your product or service will be branded as not only a direct solution to whatever problem your target market faces, but a better one than your competitors'. It can be an obvious problem or one your customers don’t realize they have. Either way, knowing your target market and their problem inside and out will ensure the solution you’re offering is satisfying that need.
When your customers are satisfied with your product or service, the likelihood of them returning increases. The best way to ensure you have satisfied customers is to create marketing and sales strategies that are specifically catered to them using product positioning. Whether they return as clients themselves or provide high-value referrals, your brand's reputation will benefit from it.
When you know what your target market is looking for, you can sell to that need using your solution’s strengths. This will result in directly filling the market gap with your solution and seeing an increase in sales because of it. The return on investment of your product positioning may not be immediate, but it can be substantial.
Implementing a product positioning process ultimately influences how your audience perceives and experiences your solution. To better understand the variety of product positioning, below we’ve listed the top four strategies found in the market today.
The most common types of positioning strategies are extensions of a product or service’s value proposition. These strategies take the strengths of a solution — whether it be competitive pricing, product characteristics, product prestige, or convenience — and place that at the center of the brand's identity.
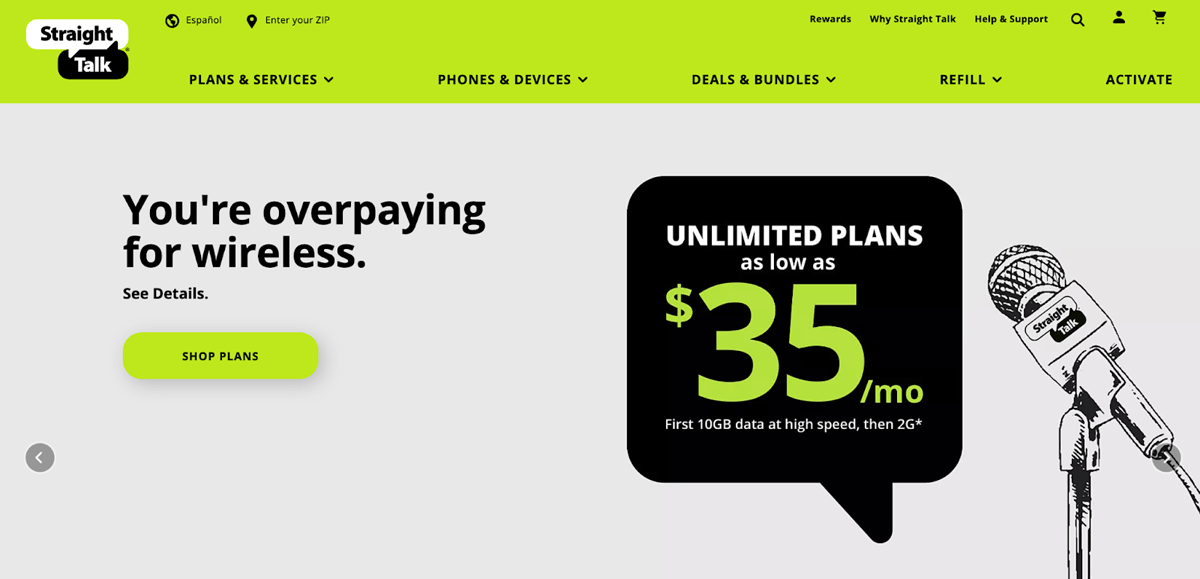
Pricing-based positioning is presenting your solution as competitive or lower in price than its competitors. Whether you're targeting B2B or B2C buyers, price is a major factor in decision making. Examples are if your solution’s total cost is competitive in the market, or if you offer payment assistance or free upgrades. Straight Talk, a phone and internet provider, does this by prioritizing their affordable plans.
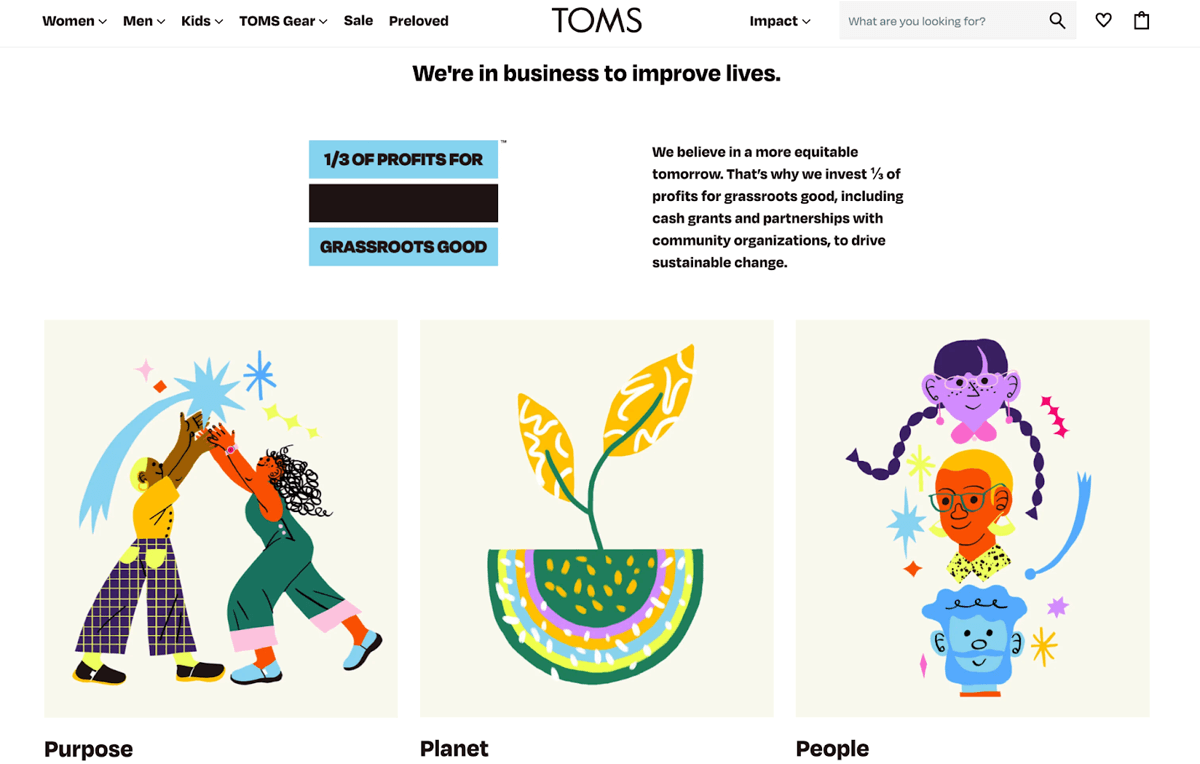
Companies using characteristic-based positioning take a feature or special attribute of their solution to place in the center of its brand identity. Common characteristics can be based in the performance, reliability, aesthetics, or sustainability of your product or service. TOMS does this by placing its sustainability efforts at the forefront of their brand.
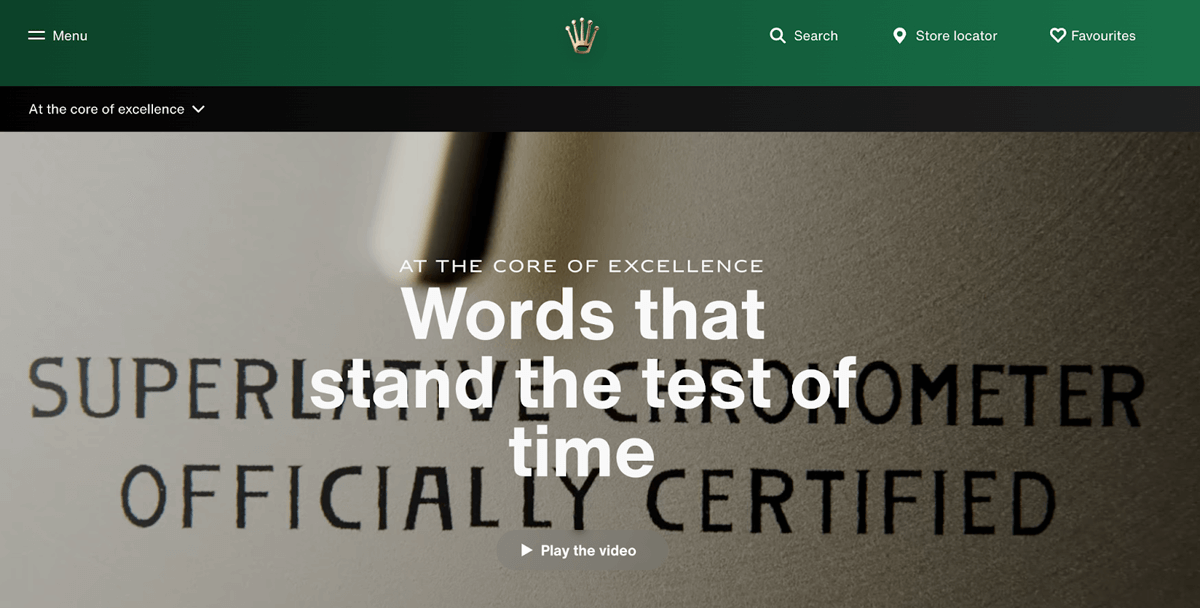
Quality-based positioning counteracts expensive solutions by branding them as prestigious or luxurious. When companies want to avoid presenting a solution on its cost alone, they'll market the solution as higher quality than its competitors, typically citing the quality or rarity of resources used to make it. Rolex has placed itself in the public’s mind as a high-end luxury watch using this positioning.

Positioning based in convenience is when companies capitalize on their product or service’s accessibility to their customers. Examples of convenience can be if the solution is geographically close to your customers or requires little effort on the buyers to access. McDonald’s uses convenience-based positioning by advertising to its customers how geographically close any restaurant is from any given location.
These product positioning strategies take the most marketable quality of your solution and use that to influence how you advertise it. They can also act as inspiration when working to identify your own unique selling proposition and product positioning strategy.
Choosing to implement product positioning into your brand identity can bring cohesiveness to your overall brand development. To do so requires extensive research into your target market, creating a positioning statement, and selecting a methodology. Complete all this before deploying any ad campaigns or sales tactics. Once a product positioning procedure is utilized, monitor your results through trackable metrics in your CRM.
A customer profile is a data-filled report with insight into your most common customer’s socioeconomics, psychological attributes, behavior, company details, geography, technology, and more. It requires considerable research in your customer history data in an effort to understand why your customers make the decisions they do.
Popular categories of data found in customer profiles are:
Once you have a customer profile, you can summarize it into a defined target market. Take all the valuable data and insight gathered in the research phase and write out a short one-liner that captures the spirit or core of the profile. For example, a streaming services company could have a target market of the following:
Movie and television lovers looking for an elevated home theater experience.
For an in-depth look into customer profiles, check out our ultimate guide including how to create your own profile with examples, benefits, and top tools to help you.
A positioning statement is an internal tool that briefly depicts who your target market is, what your product does for them, and how it’s the best option. Along with the customer profile and unique selling proposition, positioning statements should also consist of a short description of the category your solution falls under, your target audience’ need, and the main benefit your solution provides. Conveniently, you’ve completed the first step of this already.
The five steps to writing a successful positioning statement are:
Your positioning statement will act as a reference for all employees when implementing your product positioning for consistency in language and overall objectives. Continuing the streaming service example, below is a complete mock positioning statement using all five components:
For movie and television lovers (Target Audience) looking for a home-theater experience, Boothe is a subscription-based video streaming service (Category) that has over 10,000 movies and shows to choose from (Benefit). When viewers face a large vault of content (Audience Need), Boothe uses a unique and innovative AI software and user face recognition to filter movies and shows to match your exact mood in that moment (USP).
For a step-by-step guide on writing your own positioning statement, along with examples of strong statements from multiple industries and expert tips, read our article on how to write a positioning statement.
Decide if you’ll use a relative or absolute positioning methodology when presenting your brand to your market. Do this by expanding on the research you’ve done when writing your positioning statement — since you already have a USP, look into whether any other company claims a similar value proposition. The goal is to use your USP and positioning statement to identify how your solution compares to others.
If your USP is about a value proposition that other solutions have, but your solution does it better, that's relative positioning. It's comparative in nature and refers directly to your competitors. In the case your solution offers the market something that doesn't exist or isn’t accessible with other solutions, it’s absolute positioning. You’re making a claim that your product offers something entirely unique to its competitors.
The methodology you adopt can be used to influence the language and tone of your entire positioning strategy. In the case of Boothe, its USP adopts absolute positioning since no other companies use AI and face recognition software and so it may use powerful verbiage like “one of a kind,” “unprecedented,” or “unique” when creating marketing campaigns and sales content.
Boothe uses a unique and innovative AI software and user face recognition to filter movies and shows to match your exact mood in that moment.
Up to this point in building out your product positioning, you’ve been researching and creating internal tools for only your company to access. Now, marketing and sales teams will use your positioning statement and chosen methodology to deploy your positioning strategy to your target market and control how your customers actually engage with your brand.
Both marketing and sales teams use lead generating tactics to attract leads by making them aware of your solution. Since product positioning is an attempt to control how your solution is perceived, deciding how to approach marketing campaigns is two-fold. First decide how to get in front of your target audience through inbound lead generation, and then once you have their attention, how you’ll relay your product positioning and get buy-in.
The most common stages of inbound lead generation are:
If our streaming service, Boothe, were to create an ad campaign, it would make sense for it to be a commercial since they’re targeting people who enjoy watching movies and TV shows. An example plot for the commercial ad could be:
A couple is at home wanting to put on a movie before bed, but just like the night before, they can’t decide what genre they’re in the mood for. Then comes Boothe's one-of-a-kind face recognition and AI-powered movie suggestion software, which prompts movies or TV shows specifically for the couple by combining their exact moods and interests. This leaves both people satisfied with the selected film.
For more inbound lead gen strategies, check out our article on online lead generation. There you'll find eight steps to build your own process, a list of top agencies for support, benefits, and tips.
Once qualified leads are passed from the marketing team to the sales team, product positioning must extend into lead nurturing. The same messaging, language, and tone your leads were attracted to in your marketing campaigns will be what also gets them ready to make a purchase. So, when delivering your sales pitch, refer back to the positioning methodology and positioning statement you’ve adopted and keep that same attitude.
More lead nurturing activities that product positioning can be implemented into are:
When you're implementing your product positioning into your sales tactics, make sure you can deliver and back up any claims you make on behalf of your solution. Only position your products with claims and value propositions that are credible and your product can back up. Product positioning secures not only your brand identity but also your brand’s reputation.
For a breakdown of common lead nurturing stages, steps on how to create your own nurturing process, and examples, read our complete guide on lead nurturing.
Once your product positioning strategy is in place, it’s important to continuously review and analyze it. To visualize the success of your brand’s positioning, use your CRM software to organize and optimize your workflow. Set reminders to review your sales reports and results once a quarter, or more frequently if needed.
The top CRM metrics to analyze are:
If you aren’t seeing the anticipated results in response to a newly deployed positioning strategy, create a new one. The economic market, your target audience’s needs, and your product itself will develop and change over time. In response, so should your approach to product positioning.
To learn more about implementing a CRM tool into your sales process, read our article on CRM software. There you'll find the top features and benefits of a CRM as well as a guide on how to choose the right one for you.
Following these six steps will help you create, implement, and monitor a product positioning strategy that helps create and maintain a strong brand identity.
There are best practices to follow when tackling product positioning, including ideas for performing market research, using emotion as a tool, and reviewing your strategy. The following tips come from real experts who’ve been a part of creating and implementing positioning policies themselves.


Chief Finance Officer
“Be aware of the other options that clients have besides purchasing your product in order to effectively communicate what sets your offering apart. Do some research on both your direct and indirect competitors to learn how they satisfy the requirements of their respective consumer bases. Your market research should entail communicating directly with potential customers in order to collect ideas. Examples of such interactions include focus groups, surveys, and empathy sessions. This'll make it possible for you to distinguish your product from the competition and make it easier for you to explain to potential clients why your solution is the best choice to address the issues that they're experiencing.”
— James Rochester, CashBlog


Owner, CRO
“Product positioning needs to focus on how a product solves a problem. Benefits of a product must align to helping buyers solve a problem, not the features a product has. It should also convey an emotional connection to a problem, not just a logical connection. Data points, pricing, and savings trigger the logical side of the brain. That type of information is often used to justify a purchase decision, not to start a purchase decision. Starting a purchasing decision comes from an emotional connection to a problem, not a rational connection like price.”
— Ed Porter, Blue Chip CRO


Member & CTO
“To ensure that the product positioning strategy is successful, be sure to regularly review the effectiveness of the messaging being used. This includes assessing whether the content truly resonates with your customers and whether there are any changes needed. Additionally, it’s important to measure the success of the product positioning strategy in terms of sales and customer loyalty.”
— Sarah Momsen, Jit Home Buyers
These tips and tricks are worth taking into account when starting your own positioning, so adapt them as needed and see how your positioning improves.
Implementing a product positioning strategy will elevate how your brand is engaged with and experienced by your customers. The amount of research and work put into creating and deploying your strategy to your marketing and sales teams will set your brand up for success. Once you’ve gotten the attention of your target market with all the ways your solution is better than the competition, it's time to buckle down and close the deal.


Allyssa is a sales writer with a background in B2B sales and account management. After earning her degree in English and communications, she spent her selling career supporting Fortune 1000 IT and finance companies including Bank of America, Wells Fargo, and Credit Karma. As a staff writer for Selling Signals, her specialties include lead nurturing, lead generation, and sales software topics. When she's not writing or updating articles, you can find Allyssa writing poetry, traveling, or picking up any new creative hobby.

Selling Signals delivers actionable advice for sales and marketing professionals. Learn strategies that help you hit targets, strengthen customer relationships, and win more business. Get expert advice on lead generation, sales processes, CRM software, sales management, and account management directly to your inbox.
Property of TechnologyAdvice. © 2026 TechnologyAdvice. All Rights Reserved
Advertiser Disclosure: Some of the products that appear on this site are from companies from which TechnologyAdvice receives compensation. This compensation may impact how and where products appear on this site including, for example, the order in which they appear. TechnologyAdvice does not include all companies or all types of products available in the marketplace.